GET THE KCSE PREDICTION CHEMISTRY P2 MARKING SCHEMES HERE
Bunyore
1. (a) The grid below show part of the periodic table.(The letter do not represent the actual
Symbols. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
| T | Q | |||||||
| S | R | K | ||||||
| A | J | Y | U | L | ||||
| W | M | B | ||||||
| C | N | |||||||
| P | ||||||||
(i)Select the most reactive non-metal. (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
(ii)Select an elements that forms a divalent cation. (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
(iii)Element Z has atomic number 14.Show its position in the grid. (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
(iv)How do the atomic radii of U and J compare? (2mks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
(v)How do electrical conductivity of A and Y compare? (2mks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
(vi)How does the boiling point of elements K, L and M vary? Explain (2mks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
(b) The table below gives information on four elements by letters V, X, E and G. Study it and answer
the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
| Element | Electron arrangement | Atomic radius | Ionic radius |
| V | 2:8:2 | 0.136 | 0.065 |
| X | 2:8:7 | 0.099 | 0.181 |
| E | 2:8:8:1 | 0.203 | 0.133 |
| G | 2:8:8:2 | 0.174 | 0.099 |
(a) Which two elements have similar properties? Explain. (2mks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
(b) Which element is a non-metal? Explain. (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
(c) Which one of the elements is the strongest reducing agent. (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
2. (a) Petrol is a mixture of several alkane molecules ranging from pentane (C5H12) to decane (C10H22).Name the process by which petrol is obtained from crude oil. (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
(b) A decane molecule derived from petrol is cracked into hydrocarbon with equal number of carbon
atoms in each molecule.
(i) What is cracking? (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
(ii) State two conditions necessary for the above process. (2mks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
(iii) Write an equation for the cracking of decane molecule. (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
(iv) Draw and name two isomers of molecule with lower molecular mass obtained from cracking of
decane as shown in b(iii) above. (2mks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….…
(v) How would you distinguish the products formed by cracking as shown in b(iii) in the
laboratory. (2mks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
(c) Name the class to which the following cleansing agents belong.
(i) R-COONa+ (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
(ii) R- o -O-SO3Na (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
(d) Which cleaning agent above is not environmental friendly? Explain. (2mks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
3. Study the flow diagram below and use it to answer the questions that follow.

(a) Give the name and formula of the following.
(i) White precipitate E
Name………………………………………………………….. ( ½ mk)
Formula………………………………………………………. ( ½ mk)
(ii) Colourless solution F
Name ……………………………………………………….. ( 1mk)
Formula…………………………………………………….. (1mk)
(b) What property is exhibited by white precipitate E when it reacts with Sodium hydroxide and
HCl acid. (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
(c) Write an ionic equation for the reaction between white precipitate E and excess sodium
hydroxide solution. (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
(d) The information below gives the solubilities ( In g/100g of water) of substances X and Y at
various temperatures
| Temperature | 0 | 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 | 100 | |
| Solubility g/100g of water | X | 10 | 15 | 26 | 40 | 63 | 100 |
| Y | 30 | 34 | 37 | 40 | 44 | 48 |
(i) Plot a graph of solubility against temperature for the two salts X and y on the same axis. (4mks)
(i) From the graph state:
I The solubility of X at 50oC (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
II The temperature at which solubility of Y is 36g/100g of water. (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….…
III Calculate the mass of crystals of substance X which will deposit when a solution containing
50g of X in 100g of water initially at 80oC is cooled to a temperature of 30oC (1mk)
- The diagram below shows a set – up that was used to prepare oxygen gas and passing it over a
burning candle. The experiment was allowed to run for some time.
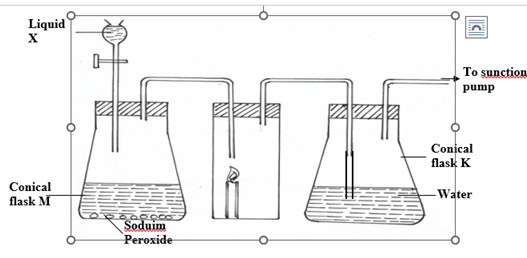
(i) Name liquid X (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
(ii) Suggest the PH of the solution in conical flask K. (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
(iii)Write an equation for the reaction taking place in the conical flask M. (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(b) During the extraction of sodium metal from sodium chloride in the Down’s cell, calcium chloride is added
(i) Explain why it is necessary to add Calcium chloride (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) Explain why sodium metal is not used in making the overhead electric cables yet it is a conductor of electricity (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
(c) (i) Describe a simple chemical test that can be used to distinguish carbon (IV) oxide and
Carbon(II) oxide gases. (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
(ii) Give one use of carbon (II) Oxide (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
(d) A form two student inverted a gas jar full of carbon (IV) oxide over water and sodium
hydroxide solution separately as shown below
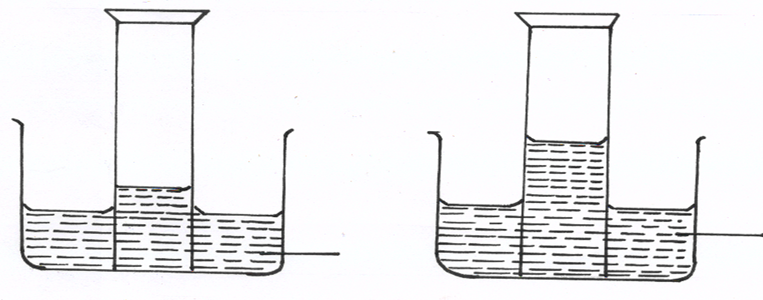
Explain the observations made. (2mks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
GET THE KCSE PREDICTION CHEMISTRY P2 MARKING SCHEMES HERE
5. (a) Study the diagram below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
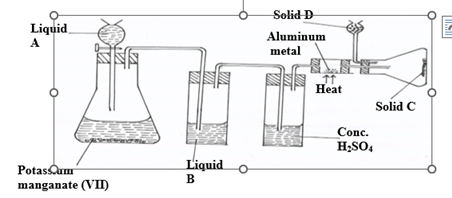
(i) Name liquids A and B
A…………………………………………………… (1mk)
B……………………………………………………. (1mk)
(ii) Suggest a suitable reagent that can be used as solid D (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
(iii) State the role of Solid D (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
(iv) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction in the conical flask (1mk)
(v) Explain why solid C collects further away from the heated aluminium metals. (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
(vi) In the combustion tube above, 0.675g of aluminium metal reacted completely with 1800cm3
of chlorine gas at room temperature. Determine the molecular formula of Solid C, given that its relative formula mass is 267 ( Al= 27.0, Cl= 35.5 molar gas volume at r.t.p = 24.0 litres) (3mks)
(b) The reaction between hot concentrated sodium hydroxide and chlorine gas produces Sodium
Chlorate (V) as one of the products
(i) Write the equation for the reaction. (1mk)
(ii) Give one use of sodium chlorate.(V) (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
(c) Explain the difference between bleaching by chlorine and bleaching by sulphuric
(IV)oxide gases. (2mks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….….
6. A. Study the diagram below that is used to prepare a gas Q.
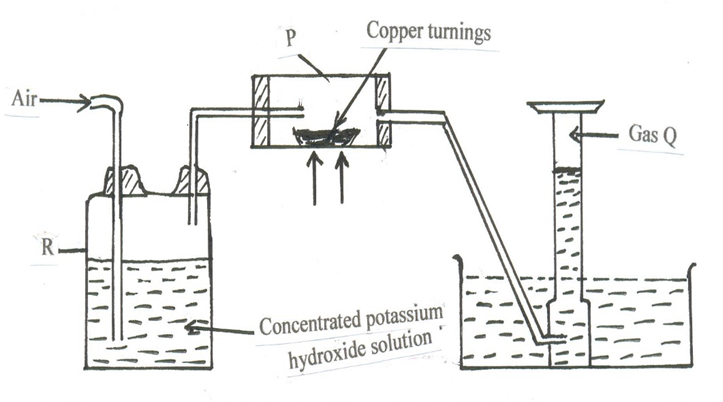
(i) (a) What component of air is eliminated in wash bottle labelled R? ( 1 mark )
(b) Write the reaction equation for the reaction that eliminates the component of air in a(i) above. (1 mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) What component of air is removed in hard glass tube labelled P? ( 1 mark )
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(iii) Identify gas Q. (1 mark )
___________________________________
B. In an experiment 1.54g of nitrogen reacted with 3.53g of oxygen to form a compound. N = 14, O = 16
(i) Calculate the moles of nitrogen and oxygen that reacted. (2 marks )
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) Determine the simplest formula of the compound formed between nitrogen and oxygen. (2 marks )
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(iii) Commend on the melting and boiling points of the compound in B(ii) above, explain. (2 marks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
7. In the preparation of Copper carbonate, copper was burnt in air and the product collected.
Dilute sulphuric acid was added and the mixture filtered and cooled. Sodium carbonate was added
to the filtrate and the content filtered. The residue was washed and dried to give a white powder.
a) Give the chemical name of the product formed when magnesium burns in air (1mk)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
b) Write a chemical equation for the formation of product. (1mk)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
c) (i) Name filtrate collected after sodium carbonate was added (1mk)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) Name the white powder. (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
d) Write chemical equation for the reaction between product in (a) and acid. (1mk)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
e) Write an ionic equation to show the formation of the white powder (1mk)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
f) Write an equation to show what happened when white powder is strongly heated. (1mk)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
g) Using a diagram, describe how a salt can be obtained from the filtrate in c(i) above (3mks)