Download Marking Scheme for Chemistry Prediction 2022-Kassu Jet
1. Study the periodic table below and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
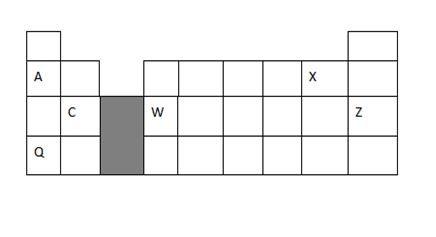
a) What type of bond exist between element C and X. Give a reason 2marks
b) How does the atomic radius of element A and Q compare 2 marks
c) C and W are both metals ,how does their electrical conductivity compare 2marks
d) Give one use of element Z 1mark
e) How is element Q stored in laboratory? Give a reason 1mark
f) Distinguish electropositivity from electron affinity 1mark
g) Identify the most reactive metal.Give a reason 2 marks
2. Carbon-14 is used to determine the age of dead organic matter. The process is known as carbon dating. The carbon in plants which is up to during photosynthesis contains small portions of radioactive carbon-14,the plant dies; the carbon-14 in the dead plant continues decaying hence the amount decreases. Carbon-14 has a half-life of about 5,600 years. During carbon dating a log of an old tree was found to have only 3.125% remaining 28,000 years after it was cut down.
(a) Fill the table to show how the percentage (%) mass of carbon-14 decreased over time 3marks
| Percentage (%) remain in mass | 100 | 12.5 | 3.125 | |||
| Time in years | 11200 | 28,000 |
(b) Using the filled table above, draw the graph of the % mass against time in years (3 marks)
(c) From the graph,
i. Determine the percentage mass that would remain after 15,000 years. (1 mark)
ii. Determine how long it would take for percentage mass to decrease to 35%. (1mark)
(d) State 2 other applications of radioactivity other than carbon dating.
(2 marks)
3. A student does some experiments to find the heat energy released when natural gas burns, uses the apparatus below

The diagram below shows the thermometer readings of one of the experiment

a. Use the readings to complete the table, entering all the values to the nearest whole number (3mks)
| Temperature of water at the start C | |
| Temperature of water at the End C | |
| Temperature change ∆T in 0C |
b. The student repeats the experiment three times. The table below shows her results.
| Experiment | Volume of gas burned in cm3 | Temperature rise of water in C |
| 1 | 1450 | 34.8 |
| 2 | 1875 | 41.2 |
| 3 | 1620 | 37.7 |
i. Calculate the amount in moles, at room temperature and pressure of methane in experiment 1. Assume that natural gas contains only methane. (M.G,V. = 24 000 Cm3) (1Mark)
ii. The quantity of heat released in experiment 1 is 29200J. Calculate the molar enthalpy change in kJ/mol for the combustion of methane. (2 Marks)
iii. The temperature rise in experiment 2 is 41.2 C. Calculate the heat change in joules in experiment 2 using the expression: Heat change in J = mass of water (in grams) ×4.2J/g/C × temperature change (2 Marks)
iv. The student uses the results from experiment 3 to calculate the molar enthalpy change in kJ/mol for the combustion of methane. She compares her value with the value in the data book.
| Students value | H=-510KJ/mol |
| Data book value | H=-890Kj/mol |
a) Explain the difference in the values above. (1 Mark)
b) The students use the table of average bond energies to calculate the molar enthalpy of combustion of methane.
| Bond | C-H | O=O | C=O | H-O |
| Average bond energy in kJ/mol | 412 | 496 | 743 | 463 |
The equation for the combustion can be shown using the displayed formulae;

Use the values from the table to calculate:
(i) The energy taken in when the bonds in the reactants are broken. (1 Mark)
(ii) Energy given out when the bonds in the products are formed (1 Mark)
(iii) Use your answers in (i) and (ii) above to calculate the molar enthalpy change for the combustion of methane (1 Mark)
4) The flow chart below shows a sequence of reactions involving a mixture of two salts, mixture X . Study it and answer the questions that follow

(a) Write the formula of the following
(i) Anion in solid Q ( 1 Mark)
(ii) Two salts present in mixture X (1 Mark)
(b) Write an ionic equation for the reaction in step Vi (1 Mark)
(c) State and explain the observation made in step (V) (3 Marks)
(d) Starting with lead (II) oxide describe how a pure solid sample of lead(II) sulphate can be prepared in the laboratory (3 Marks)
(e) How can one determine whether the solid Q obtained is pure? (2 Marks)
5)

The scheme below shows a series of reactions and compounds. Study it and use it to answer the questions that follow.
a. Identify the following compounds and products 3marks
B ………………………………………………………………………………….
C ………………………………………………………………………………….
G ………………………………………………………………………………….
b. State 2 conditions for Step 1 to occurs (1 Mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………….
c. Write an equation for the formation compound F (1 Mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………….
d. Identify reagent(s) D. (1 Mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………….
e. State the negative effect of polymer E in the environment (1 Mark)
f. State one industrial use of methane 1mark.
……………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………….
g. Draw the structure of a section of polymer E showing three repeating units 1mark
h. Name the following organic compounds. 3marks

6) The reaction scheme below shows an outline method of preparing nitric(V) acid starting with nitrogen and hydrogen as raw materials. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
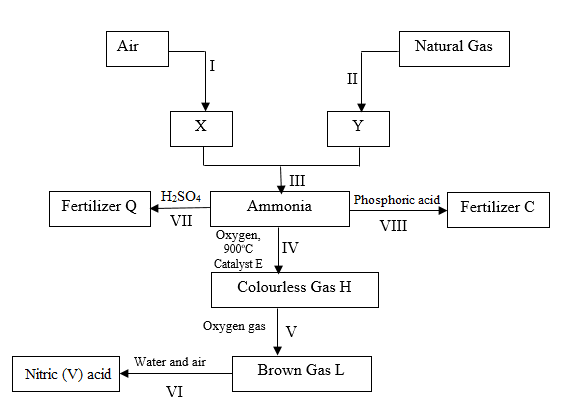
a. Identify
I. X (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………
II. Brown gas L (1 mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………….
b. Write chemical equations for reactions in steps.
I. VII (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………
II. VI (1 mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………….
c. State any two optimum conditions for the industrial process III (2 marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………….
III. Name the industrial process in step I (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………….
d. Give a reason why carbon (IV) oxide must be removed from air before obtaining X
(1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………….
e. Give one advanatge of using Fertilizer C in the place of ammonium nitrate.
(1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………….
f. Nitric (V) acid from the above process was found to have the following description in its anhydrous form.
· Density = 1.512 g cm–3
· Percentage purity = 65%
· RFM= 63
I. Calculate the concentration of nitric (V) acid, HNO3, in moles per litre. (2 marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………….
II. What will be the concentration of a solution prepared by diluting 40 cm3 of the concentrated acid to make 1000 cm3 of the acid solution? (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………
7) The set up below was used to prepare and collect hydrogen sulphide gas
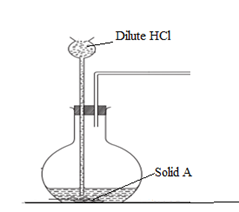
a. Complete the set up to show how the gas is collected (1 mark)
b. Identify solid A (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………
c. State the observation made when hydrogen sulphide is bubbled into a solution of Copper (II) nitrate solution. Explain (2 mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………
d. In an experiment a gas jar containing moist sulphur (IV) oxide was inverted over dry hydrogen sulphide gas
i. State the observation that made
(1 mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………
ii. Write a chemical equation for the reaction (1 mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………
iii. Why was sulphur (IV) oxide inverted over hydrogen sulphide and not vice versa (1 mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………
b) Study part of the Solvay process below and answer the questions that follow
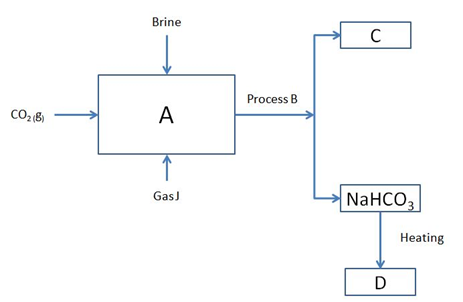
i. Identify J and C 2marks
ii. Name process B 1mark
iii. Write the equation at 2marks
a) Chamber A
b) Formation of D