GET THE KCSE PREDICTION CHEMISTRY P1 MARKING SCHEMES HERE
Bunyore
1.In the industrial preparation of oxygen, state:
(a)How dust particles are removed from air. (1 mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b)Why carbon (IV) oxide is removed before the mixture is cooled to – 250C (1 mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
2. A form four student accidentally mixed Sodium Carbonate and Calcium Carbonate. Describe
how he would obtain a dry sample of Sodium Carbonate from the mixture. (3 marks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
3. The set up below was used to prepare dry hydrogen gas. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
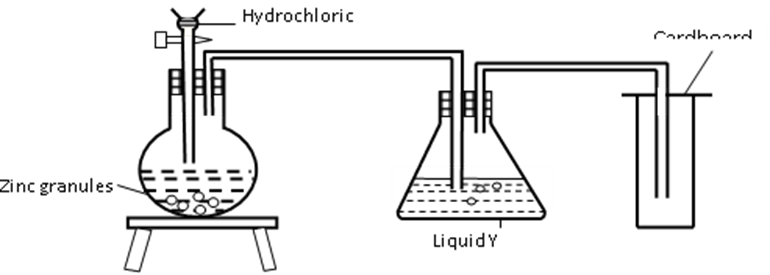
(i) Identify a mistake in the set up (1 mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
(ii) Write an equation for the reaction for the reaction that produces hydrogen gas(1 mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
(iii) State the chemical test for hydrogen (1 mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
4. When air is bubbled through pure water (pH 7), the pH drops to 6.0.Explain (2mks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
5.Explain why iron III chloride is fairly soluble in methylbenzene while Magnesium chloride is insoluble. (2 mks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
6.Describe how a solid sample of Lead(II) Chloride can be prepared using the following Reagents:Dilute Nitric Acid, Dilute Hydrochloric Acid and Lead Carbonate. (3marks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
7.50cm3 of Carbon (IV) Oxide diffuses through a porous plate in 15 seconds. Calculate the time taken by 75cm3 of Nitrogen (IV) Oxide to diffuse through the same plate under similar conditions. (C = 12, 0 = 16, N = 14) (2marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
8.(a).Carbon (IV) oxide is bubbled through Calcium hydroxide until there is no further change.
Explain using equations the changes observed. (2 marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b) Explain why diamond is used in cutting of glass and drilling. (1 mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………
9.Study the table for certain properties of substances A, B, C and D.
| Melting point 0c | Solubility in water | Electrical conduct | |
| A | -1190c | Soluble | Solution does not conduct |
| B | 10200c | Soluble | Solution conducts |
| C | 17400c | Insoluble | Doesn’t not conduct |
| D | 16000c | Insoluble | Conducts at room temperature |
Which of the substances A, B, C and D: (4 mks)
- Is a metal ……………………………………………………………………………….
- Has a simple molecular structure………………………………………………………
- Has a giant ionic structure………………………………………………………………
- Has a giant covalent structure…………………………………………………………..
10.A compound G reacts with 2 moles of bromine to form another compound whose structural
formula is.
H Br Br H
| | | |
H- C – C – C – C – H
| | | |
H Br Br H
i) What is the formula and name of compound G (2 marks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
ii) State the observations made when acidified potassium chromate (VI) is added to compound G
(1 mark)
………
GET THE KCSE PREDICTION CHEMISTRY P1 MARKING SCHEMES HERE……………………………………………………………………………………………
11.Study the set-up below and answer the questions that follow
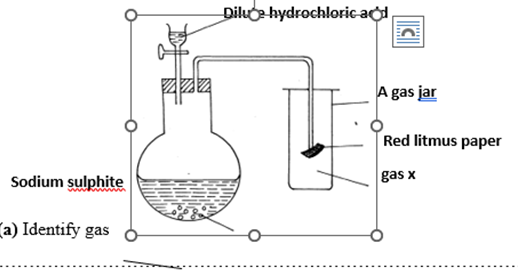
(a) Identify gas (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………
(b)Write an equation for the reaction that produces gas x. (1 mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(c) What is the effect of the gas x above on the red-litums paper (1 mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(d) State and explain two observations made when hydrogen sulphide is bubbled through a solution containing iron (III) chloride. (2mks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
12. Aluminium (III) chloride sublimes. Explain why this is possible. (2mks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
13. The table below shows the solubility of a substance at various temperatures. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
| Temperature (0C) | Solubility in g/100g of water |
| 0 | 36 |
| 40 | 30 |
| 80 | 25 |
| 110 | 20 |
(a)What is the meaning of solubility? (1 mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………
(b)What is the physical state of the substance? (1 mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………
(c)State and explain what would happen if a sample of a saturated solution of thesubstance at 400C was heated to 1100C. (1mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
14.Study the chart below and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Name:
(i) Cations present in mixture X. (1mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………
(ii) Anions present in the solution. (1mark)
(b) Write an equation to show how the white precipitate in step III is formed. (1mark)
………………………………………………………………………………….
15. Study the diagram below and answer the questions

(i) What is the process involved in step L (1mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii)Explain how process N and P can be affected (2marks)
N………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………….
P…………………………………………………………………………………….
16.The scheme below was used to prepare a cleansing agent. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Given to the type of cleansing agent prepared by the method above? (1 mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(ii)Nameone chemical substance added in step II (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
(iii)What is the purpose of adding the chemical substance named in c (ii) above? (1 mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
17. Nitrates of metals A, B, C were heated and the products of the reactions recorded in the table below.
| Nitrate of metal | Products |
| A | Metal nitrate and oxygen |
| B | Free metal, nitrogen (IV) Oxide and oxygen gas |
| C | Metal oxide, nitrogen (IV) oxide and oxygen gas |
- Name two possible identities of metal A. (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- Name the two possible identity of metal B (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- Calcium nitrate is one of the nitrate which forms the products in C. Using chemical equation show how the products are formed. (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
18. State and explain what happens to the masses of the following substances when they are separately heated in open crucibles ;(3mks)
(i)copper metal
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) Sulphurpowder
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
19.The table below gives the first ionization energies of the alkali metals.
| Element | 1st ionization energy kJ mol-1 |
| A | 494 |
| B | 418 |
| C | 519 |
- Define the term ionization energy. (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- Which of the three metals is the least reactive? Give a reason. (2mks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
20.Study the set-up below and answer questions that follow.

i) Name the gas that is produced when concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid reacts with the
Sodium chloride (1mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
ii)Why is it necessary to use a funnel in the beaker? (1mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
iii)How does the gas affect the PH of the water in the beaker? (1mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….
21. The flow chart/diagram below outlines a method of preparing a fertilizer
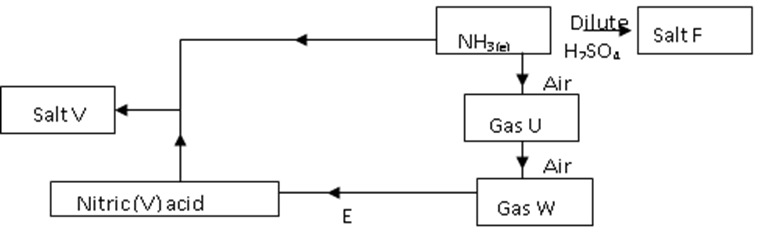
i) Identify U and W
U ……………………………………………………………. (1/2mark)
W …………………………………………………………… (1/2mark)
ii) Give the names of salt F and V
F ……………………………………………………………. (1/2mark)
V ……………………………………………………………. (1/2mark)
iii) Write a balanced equation for the formation of salt F (1 mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………….
22.(a)Draw a dot (•) and a cross (x) diagram to show bonding in Cl2O. (1 mark)
b) Explain why the compound Cl2O has a very low melting and boiling point. (1 mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
23.Ethene reacts with oxygen according to the equation.
C2H4(g) + 3O2(g) 2 C02(g) + 2H2O (g)
15.0 cm3 of ethene were mixed with 50cm3 of oxygen and mixture was sparked to complete the reaction. If all the volumes were measured at a pressure of one atmosphere and 250C. Calculate the volume of resulting gaseous mixture. (3 marks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
24. The graph below shows the behavior of a fixed mass of a gas at constant temperature.
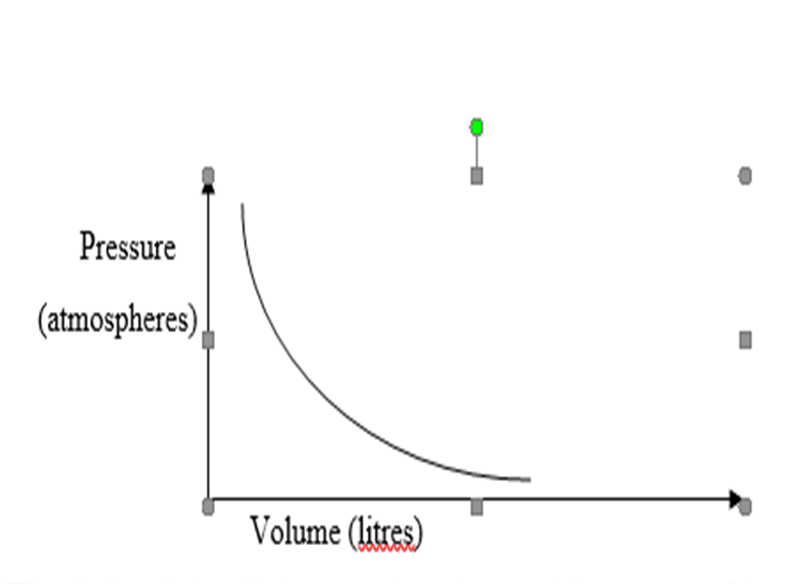
- What is the relationship between the volume and the pressure of the gas? (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
- 3 litres of oxygen gas at 1atm atmosphere pressure were compressed to 2atm at constant temperature. Calculate the volume occupied by the oxygen gas. (2marks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
25.Temporary water hardness can be removed by boiling
(a)What is hard water.(1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b)Write a chemical equation to show how temporary hardness is removed by boiling. (1 mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(c)State one advantage of hard water. (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
26.A student set-up the experiment below to collect gas K. The glass wool was heated before heating the zinc powder.

27. During the extraction of lead from its ores one of the main ore used is Galena
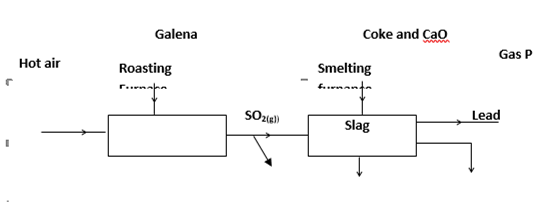
(i) Write an equation for the reaction in roasting furnace. (1 mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) Name gas P (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………
(iii) State one use of lead metal. (1 mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
28. The empirical formula of a compound is CH2 and it has a molecular mass of 42.
(a) What is the molecular formula of this compound? (1 mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Write the general formula of the homologous series to which the compound belongs.(1mk)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
- Draw the structural formula of the third member of this series and give its IUPAC name.
(1mark)